LeetCode in Cpp
2. Add Two Numbers
Medium
You are given two non-empty linked lists representing two non-negative integers. The digits are stored in reverse order, and each of their nodes contains a single digit. Add the two numbers and return the sum as a linked list.
You may assume the two numbers do not contain any leading zero, except the number 0 itself.
Example 1:
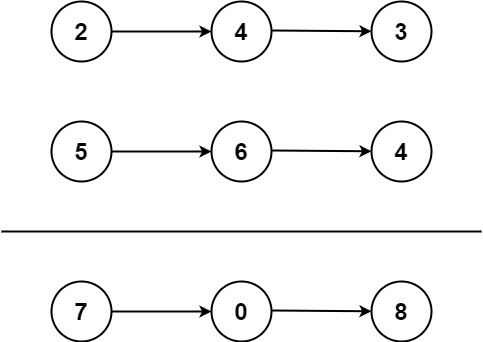
Input: l1 = [2,4,3], l2 = [5,6,4]
Output: [7,0,8]
Explanation: 342 + 465 = 807.
Example 2:
Input: l1 = [0], l2 = [0]
Output: [0]
Example 3:
Input: l1 = [9,9,9,9,9,9,9], l2 = [9,9,9,9]
Output: [8,9,9,9,0,0,0,1]
Constraints:
- The number of nodes in each linked list is in the range
[1, 100]. 0 <= Node.val <= 9- It is guaranteed that the list represents a number that does not have leading zeros.
Solution
/**
* Definition for singly-linked list.
* struct ListNode {
* int val;
* ListNode *next;
* ListNode() : val(0), next(nullptr) {}
* ListNode(int x) : val(x), next(nullptr) {}
* ListNode(int x, ListNode *next) : val(x), next(next) {}
* };
*/
class Solution {
public:
ListNode* addTwoNumbers(ListNode* l1, ListNode* l2) {
ListNode* dummyHead = new ListNode(0);
ListNode* p = l1;
ListNode* q = l2;
ListNode* curr = dummyHead;
int carry = 0;
while (p != nullptr || q != nullptr) {
int x = (p != nullptr) ? p->val : 0;
int y = (q != nullptr) ? q->val : 0;
int sum = carry + x + y;
carry = sum / 10;
curr->next = new ListNode(sum % 10);
curr = curr->next;
if (p != nullptr) {
p = p->next;
}
if (q != nullptr) {
q = q->next;
}
}
if (carry > 0) {
curr->next = new ListNode(carry);
}
return dummyHead->next;
}
};

